Diplopia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
What is Diplopia?
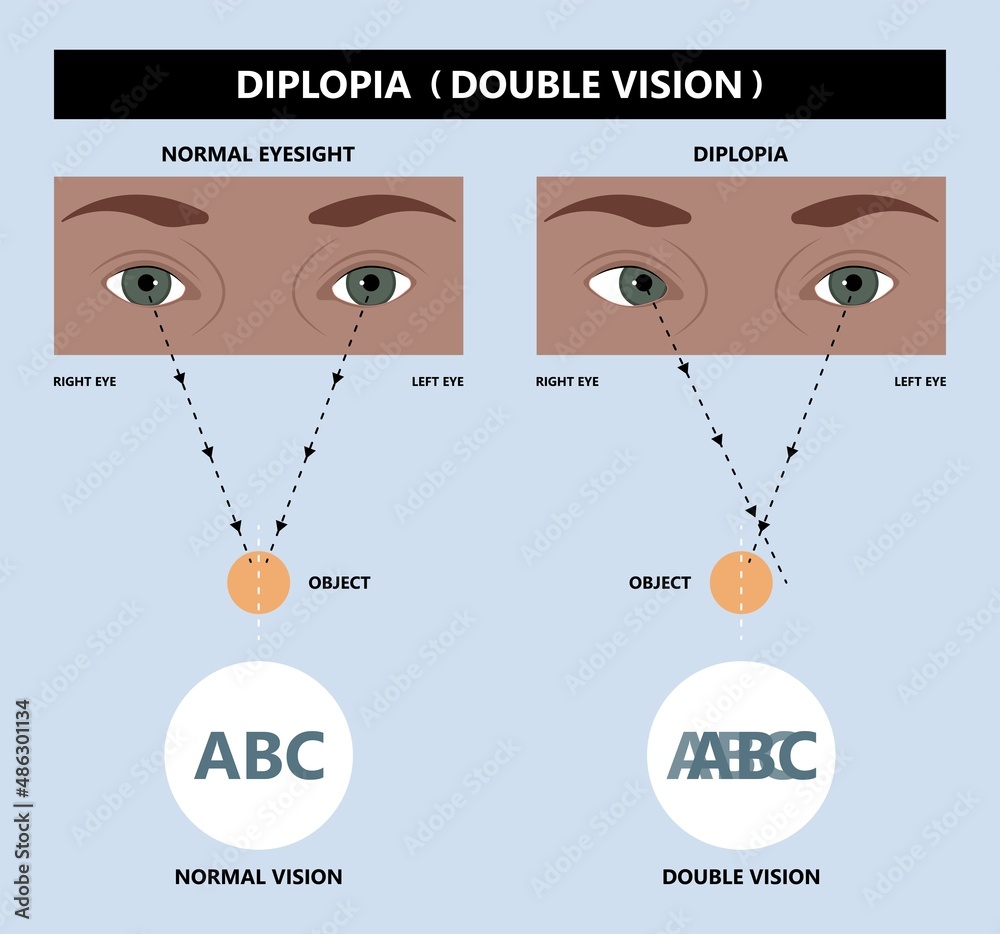
Diplopia, commonly known as double vision, is a visual condition in which a person sees two images of a single object. It occurs when the eyes are unable to align properly, causing the brain to receive conflicting visual signals.
Causes of Diplopia
Diplopia can be caused by various factors, including:
- Weakened eye muscles
- Eye injuries or trauma
- Neurological disorders
- Eye conditions such as astigmatism or cataracts
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of diplopia include:
- Seeing two images instead of one
- Images appearing side by side, on top of each other, or at an angle
- Eye strain or discomfort
- Headaches
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to consult with an eye specialist for a proper diagnosis. They will conduct a comprehensive eye examination to determine the underlying cause of your diplopia.
Treatments for Diplopia
The treatment of diplopia depends on the underlying cause. It may include:
- Wearing corrective lenses or using prisms
- Eye exercises to improve muscle coordination
- Medications to address underlying conditions
- In some cases, surgery may be required
Your eye specialist will recommend the most appropriate treatment option based on your specific condition.